Open-source robots for sustainable, fossil-free farming
Mission: Build and share autonomous robotic systems that boost crop production, reduce environmental impact, and remain fully accessible to researchers, farmers, and innovators.
Agroecology Lab designs and builds open-source autonomous robots for agroecological and mainstream farming systems.
The goal is to replace fossil-fuel-intensive field operations with lightweight, solar-powered, cooperative robots that can be built, modified, and deployed without proprietary lock-in.
Why it needs to exist
Industrial agriculture optimises for scale, not resilience. Agroecological systems fail to scale because labour and tooling do not exist at field level.
This lab exists to close that gap by providing open, reproducible robotic tools designed for small-scale, diverse cropping systems.
What success looks like
- Robots that operate continuously in real fields, not lab conditions
- Zero proprietary dependencies in hardware or software
- Designs that can be replicated by others with modest resources
- Demonstrated reduction in labour and fossil fuel inputs
Who it is for
- Researchers working on agroecology and field robotics
- Farmers experimenting with low-input systems
- Engineers interested in open hardware and autonomy
Open Core;
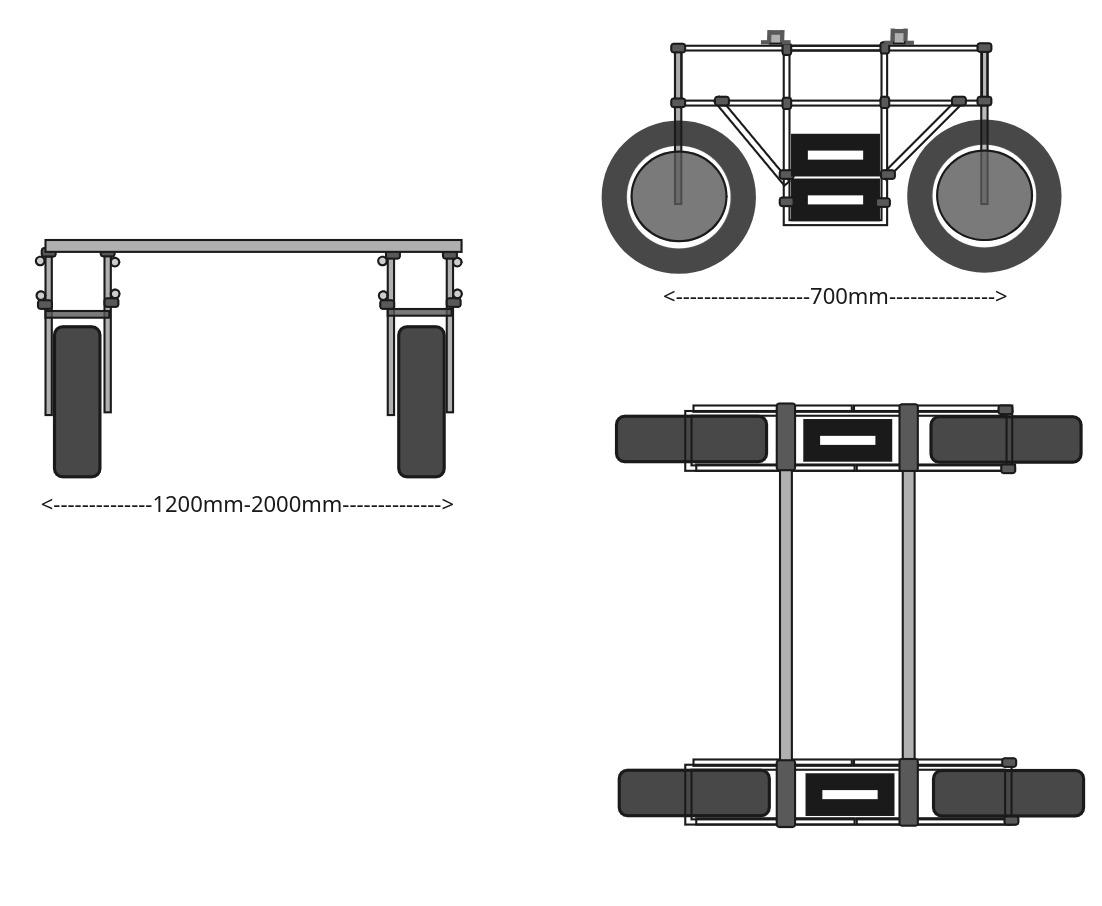
A fully open-hardware robot compute unit built around a stackable 10 cm × 10 cm module standard.
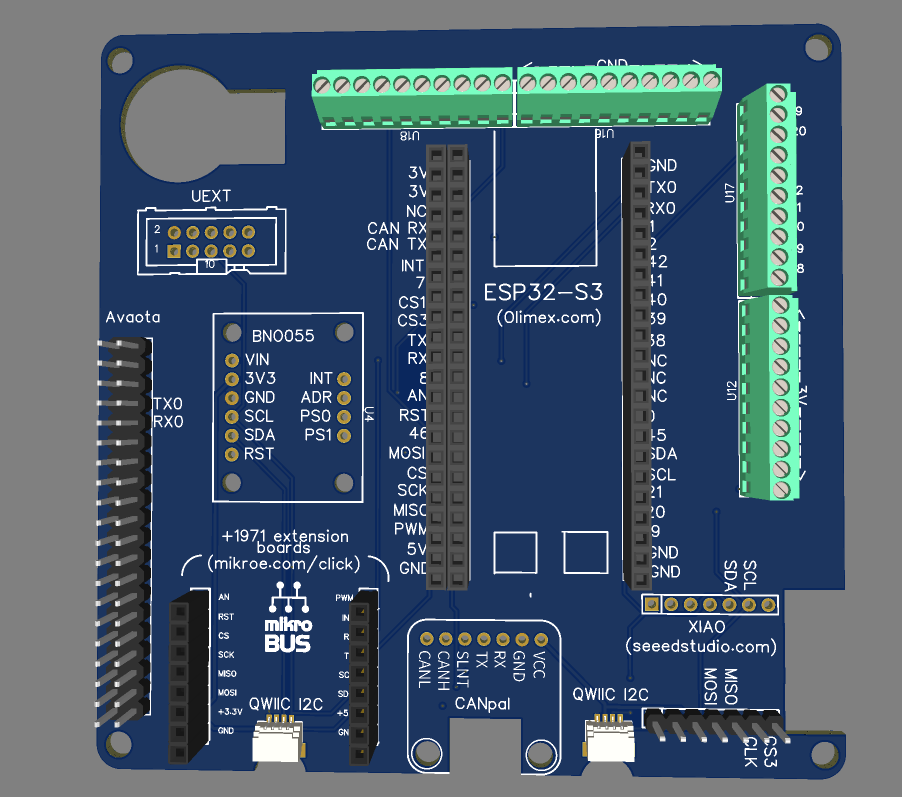
The core combines one or two octa-core ARM Cortex-A55 processor with onboard AI acceleration for perception and autonomy, paired with an ESP32-S3 microcontroller for deterministic real-time control.
Native CAN bus support enables robust field-level communication. Dual GNSS RTK receivers provide centimetre-scale positioning for navigation and task execution.
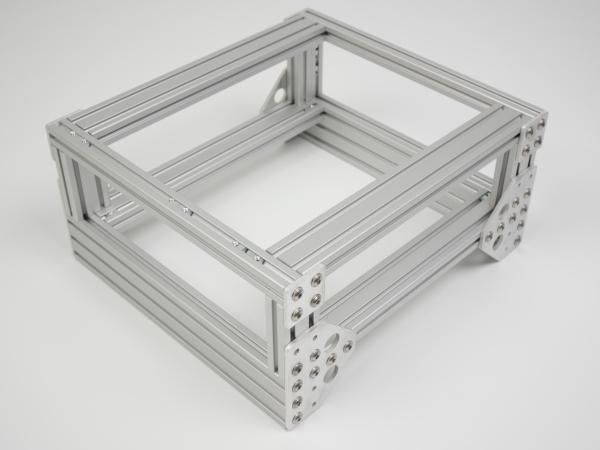
All schematics, PCB layouts, and firmware are released under open licences. The system is housed in a rugged, waterproof aluminium enclosure with M12 connectors, designed for long-term outdoor deployment.
| Photo | Component | Description | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
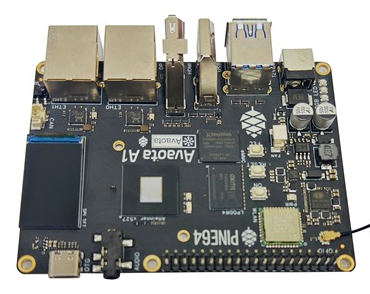 | Yuzuki Avaota-A1 SBC | Octa-core 64‑bit ARM Cortex‑A55 (up to 1.8 GHz), 4 GB RAM, integrated AI accelerator. Open‑hardware platform. | 2 |
|
ESP32‑S3 Microcontroller | Real-time Lizard control node and general‑purpose peripheral I/O on custom open hardware PCB. | 1 |

|
BNO055 IMU | Adafruit 9-DOF Absolute Orientation IMU Fusion Breakout – BNO055 | 1 |

|
CAN Bus Breakout | CAN interface breakout for deterministic, vehicle‑grade communication. | 1 |

|
SparkFun GNSS RTK or alternate Septentrio Mosaic |
High‑precision GNSS positioning with RTK support. | 2 |
|
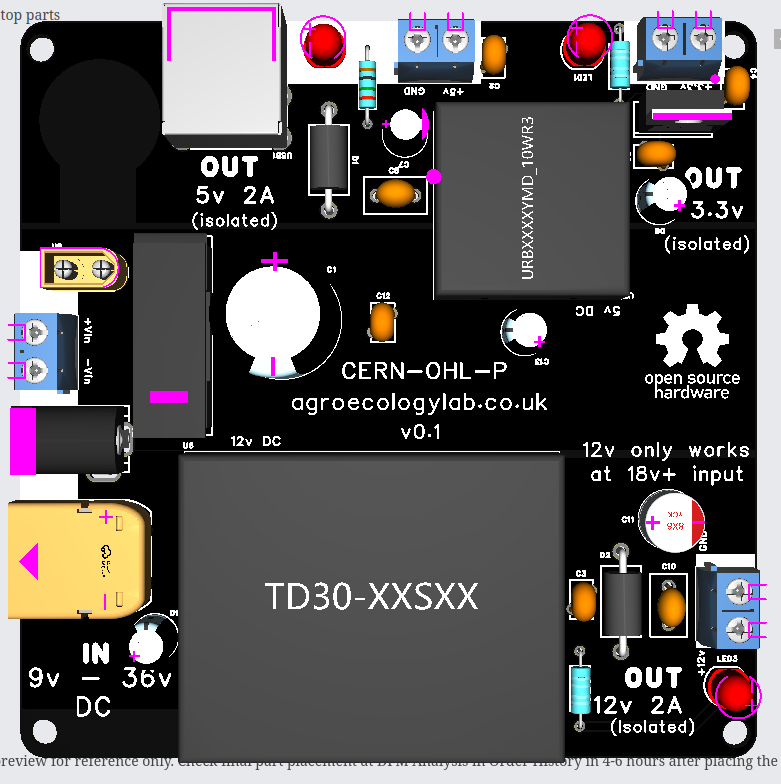
36V → 12V & 5V Power Conversion & Isolation from motor noise | Custom‑fabricated power regulation and electrical isolation board. | 1 |

|
Waterproof Aluminum Enclosure | Sealed aluminum enclosure with M12 connectors for rugged deployments. | 1 |
Open AgBot
The Open AgBot Platform integrates high-performance motors, precise control, long-lasting batteries suitable for Low temp <0C charging and rugged suspension into a fully modular, open-hardware agricultural robot.
Modular chassis and standardised connections enable rapid expansion and reconfiguration, providing full control over electronics, software, and mechanics for a versatile, field-ready system.
| Photo | Component | Description | Qty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Odrive CAN Bus Drivers with (Open hardware version, in development) | High-performance motor control with real-time CAN communication for precise torque and speed regulation. | 2 | |
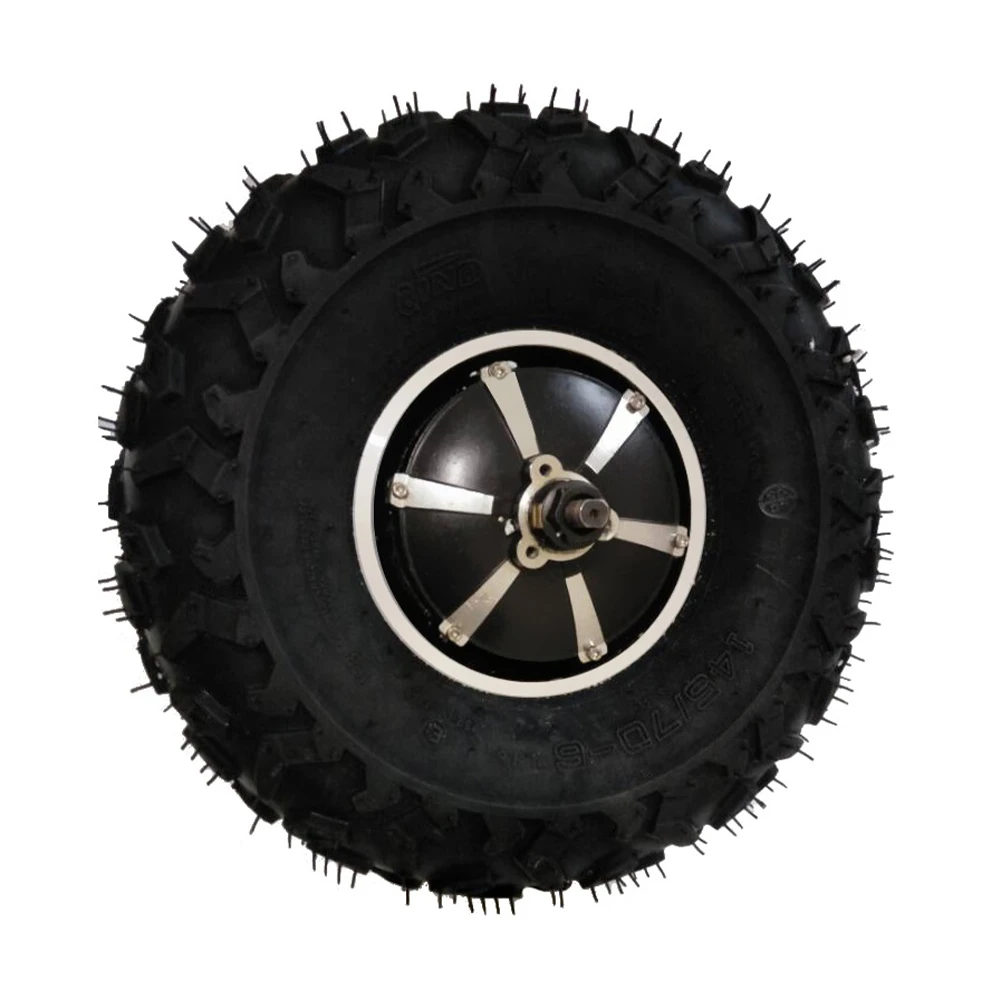 | 500W Hub motor | Geared hub motors 100N.m with 4096*10 encoder delivering good acceleration and traction. | 4 |
 | 32 V Sodium-Ion Battery Packs | High-capacity energy modules providing long-duration power for fully autonomous operation. | 6 |
 | 5″ Fatbike Suspension Forks | Shock-absorbing suspension for smooth navigation across rough terrain and dynamic environments. | 4 |
 | Modular Chassis Structure | Lightweight aluminium tube sections forming a flexible backbone for sensors, processors, and actuators (round tube typically ~40 mm OD, ~37 mm ID). | Many |
 | Chassis Connectors | Aluminium 90° crossover and modular pipe fittings used to join tubing at right angles for structural frames. | Many |
Open AgBot Mini (WIP)
A 1/4 scale development platform for testing and validation
| Dev platform Components | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Driver | Odrive | 2 |
| Electric wheel | Nema17 BLDC | 4 |
| Chassis structure | 1515 extrusion | many |
| Chassis connections | 1515 corner | Many |
Software stack(s)
Lizard
The Open AgBot Platform leverages Lizard developed by Zauberzeug for real-time robot orchestration, using its framework to manage sensor input, motor control, and navigation. Lizard enables seamless communication between the processor, microcontrollers, and peripherals, coordinating autonomous operations while remaining fully open and customisable. Lizard supports a range of motor drivers
RoSys
On top of Lizard, developers can use RoSys, an asyncio-based Python framework, to simplify control loops, messaging, and UI, providing the fastest route to a working robot. The agricultural implementation, Field Friend, builds on RoSys to coordinate autonomous navigation and field operations.
DevKit ROS
As an alternative to RoSys, developers can choose DevKit ROS, a full ROS‑based development kit tailored to the Open AgBot Platform. DevKit ROS provides standard ROS tooling, sensor drivers, simulation support and community interoperability, making it ideal for teams already invested in the ROS ecosystem or requiring mature libraries for perception and planning. We are working on a Docker image for this
Quick start Setup
Check readme
Docker
To publish your changes as a Docker after making local changes run
publish.sh samuk/basekit-ros:latest
Adjusting for your Docker account.
Safety
The proposed motor drivers have e-stop functionality. This will be enhanced with human presence detector modules.
Our work includes developing autonomous field robots for tasks such as precision weeding and harvesting, alongside developing LoRa mesh and RTK-based communication networks for robust telemetry in rural settings.
The problem
In agricultural robotics the “small rover trap” burns out both capital and talent, and because the IP is siloed, each new team starts from scratch. Fragmented development efforts and proprietary systems prevent efficient innovation and scaling.
Aim
An open, modular hardware + software platform for agricultural robotics — enabling farmers, startups, and researchers to innovate without constantly rebuilding the basics (chassis, drive system, ROS2 integration).
- An open-source agricultural robotics platform integrating key software projects into a coherent containerised stack.
- Documenting two open hardware reference platforms running the stack, a small development rover and a full scale agricultural rover.
Benefits
- Farmers: affordable, non-vendor-locked automation.
- Startups: reduced burn, faster prototyping, focus on unique value.
- Researchers: reproducibility + collaboration.
- Industry: larger ecosystem, interoperability, reduced fragmentation.
We are keen to contribute real-world use cases, test scenarios, and field conditions from small-scale, diversified agriculture, and to collaborate on shaping technologies that improve resilience and communication in remote agroecological systems. For project aims & rationale see bottom of page.
Project v1.0 – Human following super-barrow
The first project is to follow a human around, farmers, particularly small scale ones spend a lot of time walking, carrying things. “People spend as much as 20%-30% of their time picking in the field actually walking up and down these picked rows” Burrow
Project v2.0 – Mechanical weeding between crop rows
The project is to test and validate the Visual servoing code and integrate it into Farmbot-ROS code. Using visual servoing as the local planner & Farmbot-ROS as the global planner / GPS waypoint follower.
The robot will pull simple mechanical hoe between the crop rows
Project v3.0 – Automated charging
Automatic charging. Development of Navigation and mechanical components to enable the robot to return to a charging dock
Project v4.0 – Delta weeding
This will enhance the weeding capability using a AI driven Delta robot to enable more accurate weeding
Project v5.0 – Harvesting baby leaf
Using Quick cut greens harvester attachment
Project v6.0 – Open data publishing
Publishing open data
Papers & reference code
Vins-fusion
StellaVslam
https://gitlab.com/charles.fox/r4pcb